NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
Meghan Markle is being dragged back into another legal battle with her estranged half-sister.
In 2022, Samantha Markle sued the Duchess of Sussex for allegedly defaming her in multiple interviews, including a 2021 tell-all with Oprah Winfrey. The case was dismissed with prejudice in 2024, which means Samantha cannot file the claims again. The elder sibling appealed the dismissal, and an oral argument has been scheduled for Sept. 9 in Jacksonville, Florida, Fox News Digital has learned.
Royal expert Ian Pelham Turner told Fox News Digital this family feud casts a dark cloud over the Sussexes, especially Harry, who is reportedly attempting to reconnect with his family.
PRINCE WILLIAM’S ABSENCE AT KING CHARLES AND PRINCE HARRY’S ‘PEACE SUMMIT’ COULD BE A ‘WARNING SHOT’: EXPERT
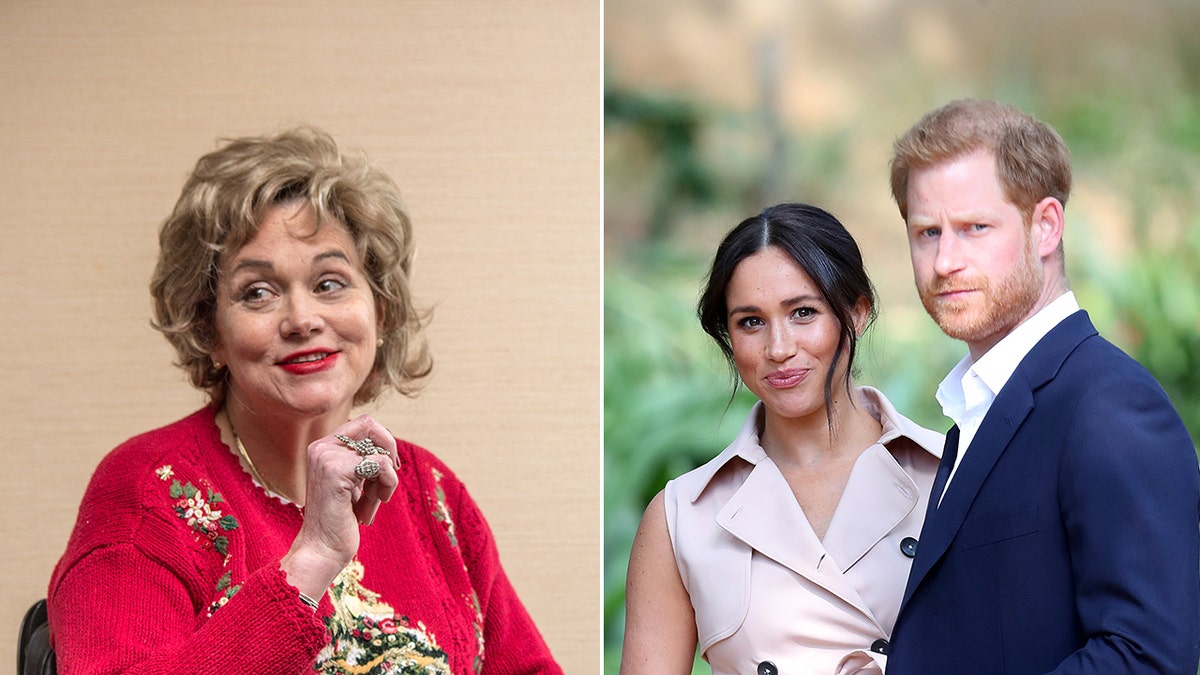

Samantha Markle, left, claimed that she was defamed by her estranged half-sister Meghan Markle. The Duchess of Sussex won the defamation lawsuit brought forward by her sibling. (MEGA/Getty Images)
“More legal disputes between Meghan and Samantha could break the fragile links between Harry and Meghan trying to establish a way forward,” Turner warned. “The royals are hyper-sensitive toward any legal issues in America, resulting in any more secrets coming out to the detriment of the royals in the U.K.”
“This could be misconstrued as a timely action by Samantha Markle as she sees her half-sister on the ropes regarding Netflix and a glimmer of hope to be reconnected with the royal family.”

Meghan Markle has been estranged from the paternal side of her family since she married Prince Harry in 2018. (Karwai Tang/WireImage/Getty Images)
British royals expert Hilary Fordwich told Fox News Digital that another high-profile dispute involving Meghan will likely make other senior royals worried. The royal family has stayed faithful to the late queen’s mantra – never complain, never explain.

In her lifetime, Queen Elizabeth II followed the mantra “never complain, never explain.” (Alastair Grant – WPA Pool/Getty Images)
“There is nothing good about this for Meghan Markle,” said Fordwich. “Her reputation is tarnished further by her own sister making such allegations. Whether true or not, it doesn’t matter, as neither way does it reflect well.”
A spokesperson for the duchess, 44, told Fox News Digital they will not be commenting.

Meghan Markle has been attempting to make her mark as an entrepreneur this year. (Karwai Tang/WireImage/Getty Images)
In a statement sent to Fox News Digital, Samantha’s lawyer, Peter Ticktin, said: “The District Court judge, an Obama appointee, dismissed the lawsuit brought by Samantha Markle against her sister Meghan Markle, finding that there was no case. This decision was wrong, and now, we are tasked with convincing a three-judge panel of the 11th Circuit Court of Appeals of how our case was solid.”
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR THE ENTERTAINMENT NEWSLETTER
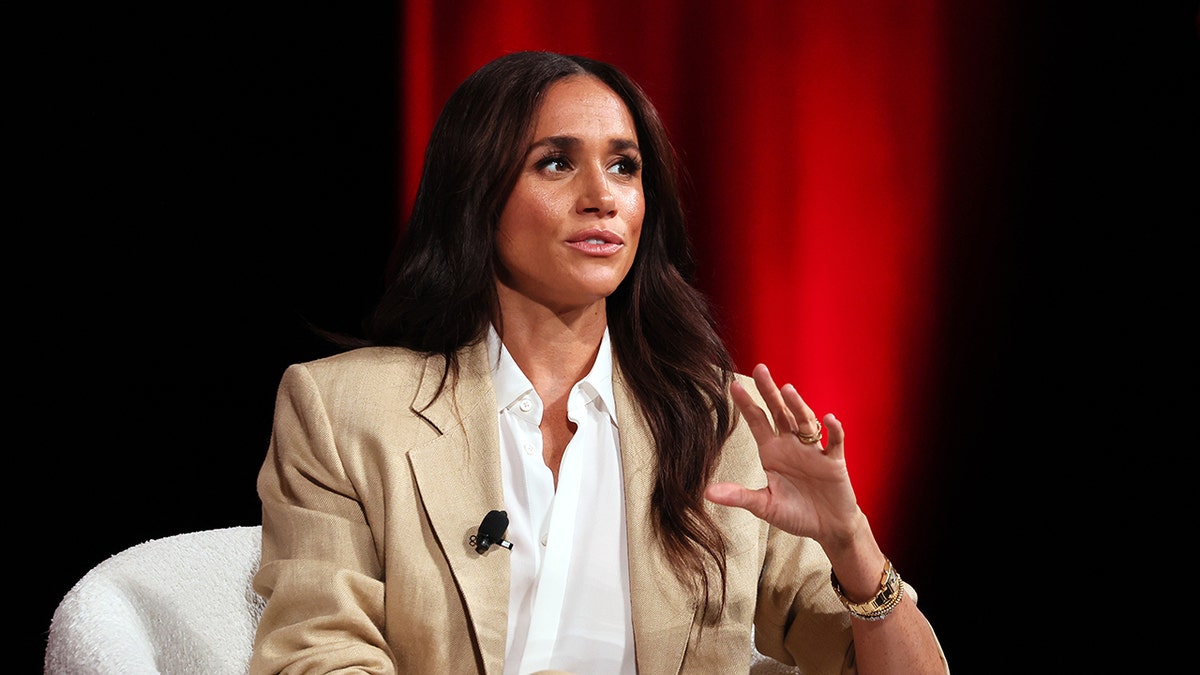

Meghan, Duchess of Sussex speaks onstage during the Time100 Summit at Jazz at Lincoln Center on April 23, 2025, in New York City. The Duchess has previously spoken out about her half-sister Samantha Markle and their father, Thomas Markle, speaking to the British press. (Jemal Countess/Getty Images for Time)
“Of course, we differ from the District Court judge, or we would have never brought the case in the first place,” said Ticktin. “We are hoping and somewhat expecting that the panel of three judges on the 11th Circuit Court of Appeals will see the error by the lower court and reverse the dismissal.”
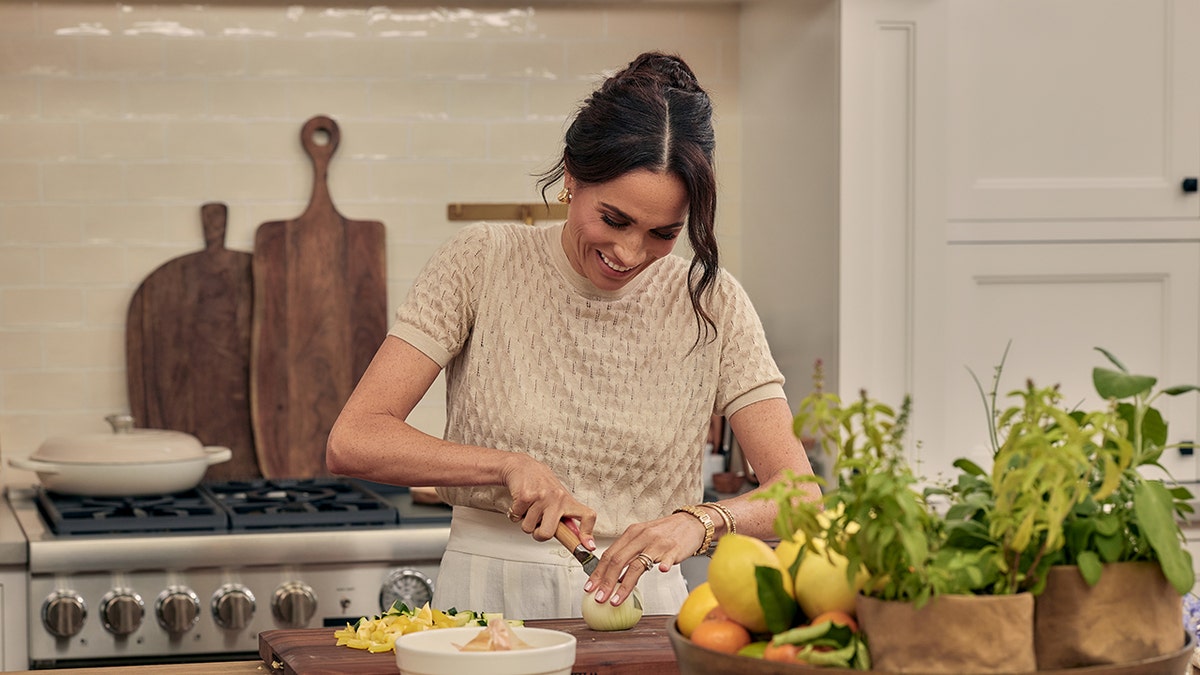

Meghan Markle’s lifestyle products were featured in her Netflix series, “With Love, Meghan.” (Netflix)
Doug Eldridge, a branding expert and the founder of Achilles PR, told Fox News Digital that such public disputes with family members will continue to overshadow Meghan’s efforts to boost her reputation. The “Suits” alum launched a lifestyle brand, As Ever, and her Netflix series, “With Love, Meghan,” this year.

Prince Harry and Meghan Markle shared their love story and struggles with royal life in the 2022 Netflix docuseries “Harry & Meghan.” (Netflix)
“Harry was very close to his mother and brother, while Meghan had seemingly been estranged from her father and half-siblings for years,” said Eldridge. “When there is a public breakup of a beloved family, like Harry and the Windsors, it creates a polarizing vacuum. On top of that, when someone is seen as the… negative variable (as Meghan was either credited or blamed, depending on your perspective), it intensifies that polarization to near-acerbic levels.”
“So far, Meghan has kept her family… at arm’s length,” he continued. “Sadly, changing that at this point would alter the entire narrative she worked to build and, with it, deepen the cracks in an already shaky brand foundation she’s trying to fortify.”

Meghan Markle at the Variety Power of Women Los Angeles presented by Lifetime at Mother Wolf on Nov. 16, 2023, in Los Angeles. (Michael Buckner/Variety via Getty Images)
After the couple made their exit from the U.K. in 2020, they aired their struggles with royal life. Harry’s 2023 memoir “Spare,” which shared embarrassing details about the House of Windsor, worsened his relationship with the royal family. Royal experts previously claimed to Fox News Digital that Harry and his older brother, Prince William, weren’t on speaking terms.
LIKE WHAT YOU’RE READING? CLICK HERE FOR MORE ENTERTAINMENT NEWS

Prince Harry and Prince William are said to not be on speaking terms. (Samir Hussein/WireImage/Getty Images)
In May, Harry told the BBC he wanted to reconcile with his family, but his father wouldn’t speak to him. His father, King Charles III, was diagnosed with an undisclosed form of cancer in February 2024.
“I would love reconciliation with my family,” said the 40-year-old. “There’s no point in continuing to fight anymore. I don’t know how much longer my father has.”
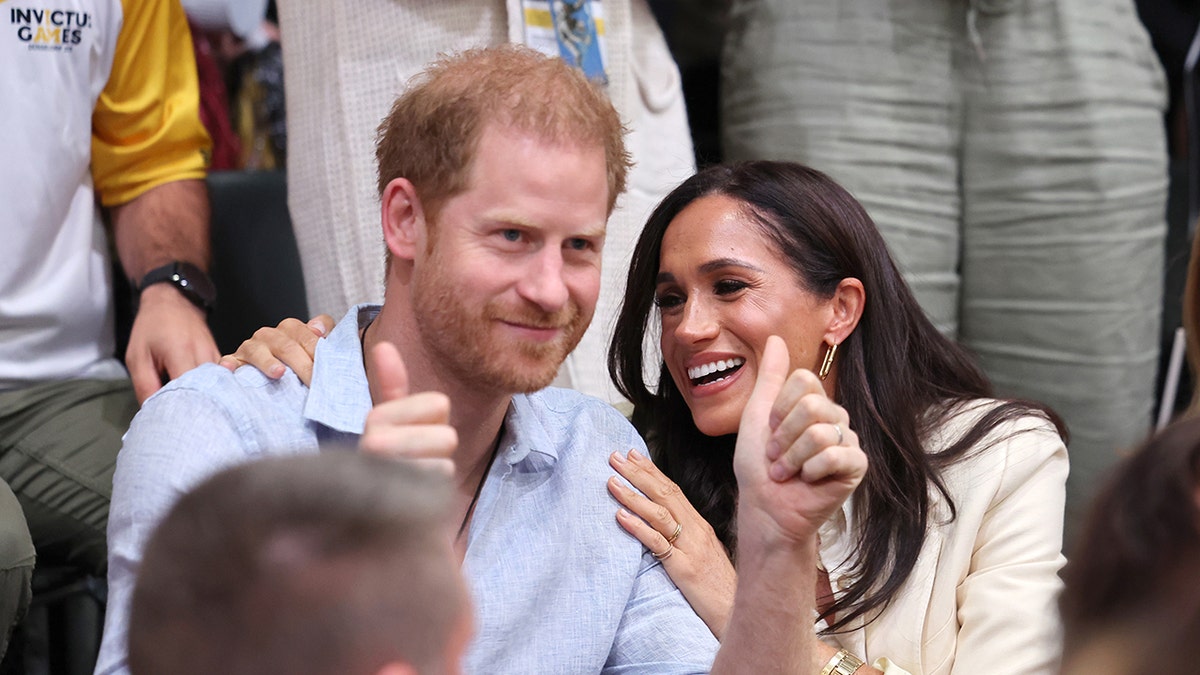

Reports of a “peace summit” sparked rumors that Prince Harry was on his way to reconciling with his family. (Chris Jackson/Getty Images for the Invictus Games Foundation)
The Mail on Sunday reported that Harry’s aides had a private meeting on July 9 with the king’s communications secretary in London. Representatives for Buckingham Palace and the Duke and Duchess of Sussex did not immediately respond to Fox News Digital’s request for comment at the time.
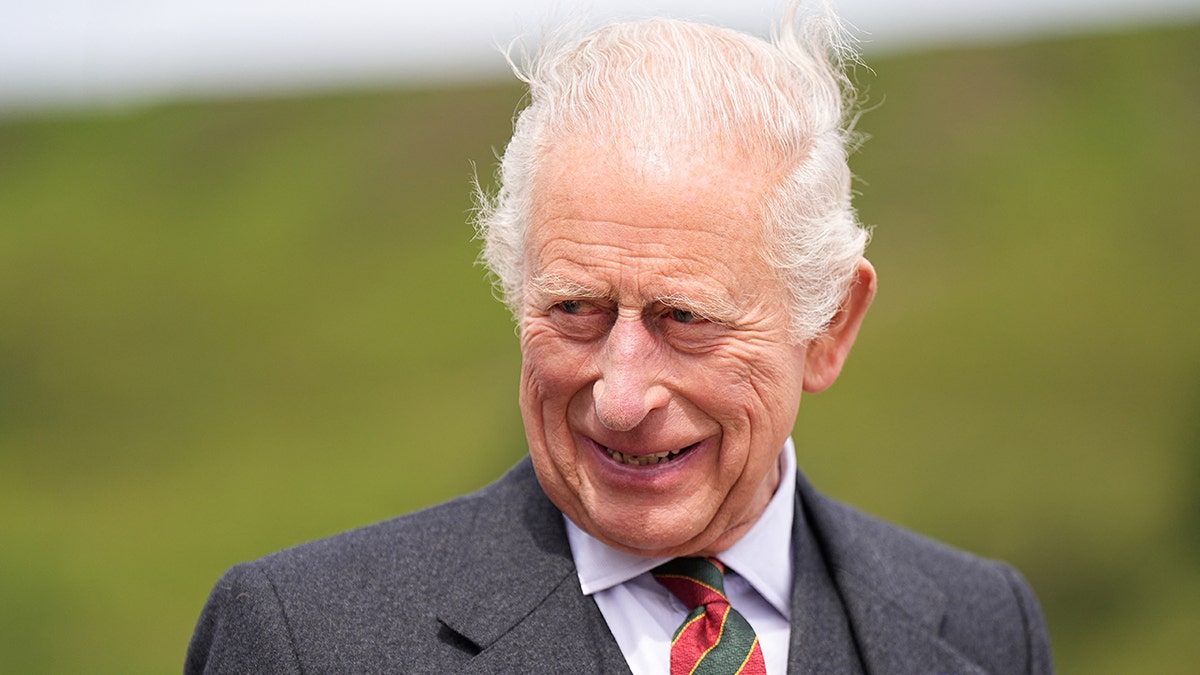

Britain’s King Charles III smiles upon arrival to attend a reception at Scrabster Harbour in Thurso, northern Scotland on July 28, 2025. The monarch was diagnosed with an undisclosed form of cancer in 2024. (Aaron Chown/Pool/AFP via Getty Images)
But Meghan’s latest dispute with her estranged sister could potentially make the royal family wary of any future peace talks.
“As is common practice… Samantha was permitted to amend her complaint against her half-sister when it was challenged by a motion to dismiss twice,” Jonna Spilbor, a criminal defense and family law attorney, told Fox News Digital.
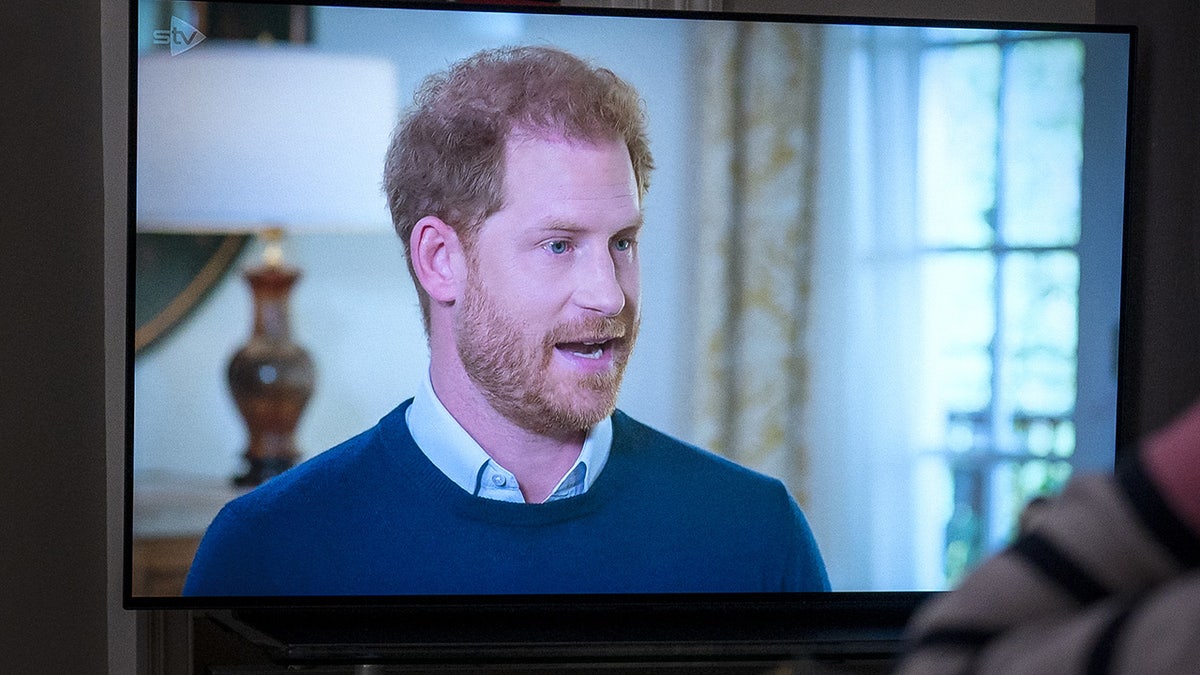
A person at home in Edinburgh watches the Duke of Sussex being interviewed by ITV’s Tom Bradby before his controversial autobiography “Spare” is published in 2023. (Jane Barlow/PA Images via Getty Images)
“Ultimately, the lawsuit failed and was dismissed with prejudice, meaning it was dead,” Spilbor explained. “However, Samantha’s legal team appealed that dismissal. It appears Samantha’s team received some relief from the appellate court, which has set a hearing to allow Samantha to attempt to convince the court that the case should be revived.
“So, the reason Meghan is being dragged back to court on a case that was given a death sentence at the trial court level is that the appeals court is performing CPR. The case may die another day. But that won’t be determined until after the hearing.”
WATCH: MEGHAN MARKLE ‘MOVED ON’ FROM ROYAL FAMILY DRAMA, AUTHOR CLAIMS
Meghan is not expected to appear at the hearing.
Samantha, 60, claimed in her original filing that Meghan made defamatory statements during her interview with Winfrey when she said she “grew up as an only child,” People magazine reported. Samantha argued that she and Meghan “were close during childhood” but drifted after Meghan started dating the British prince.

Meghan Markle, an American actress, became the Duchess of Sussex when she married Britain’s Prince Harry in 2018. (Jonathan Brady – WPA Pool/Getty Images)
According to the outlet, Samantha also claimed there were defamatory implications when Meghan said during that same interview that Samantha “changed her last name back to Markle” after she began dating Harry. Honeywell determined in a 2023 ruling that telling Oprah she “grew up as an only child” was a protected opinion.
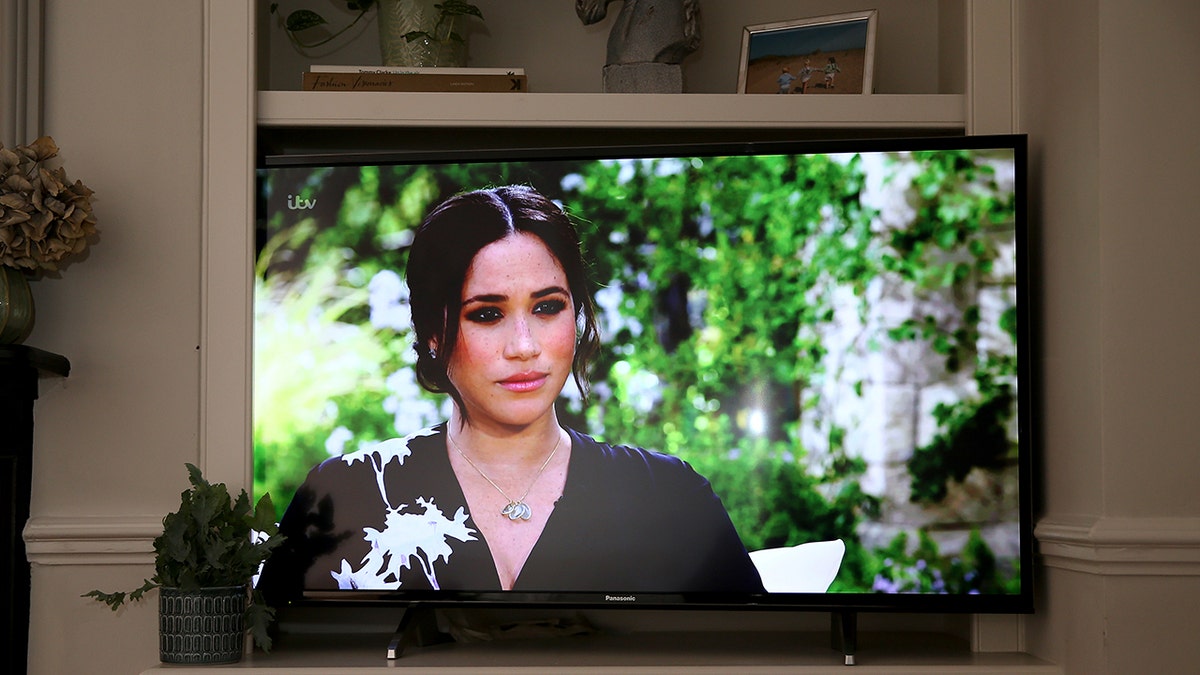
Meghan, Duchess of Sussex, being interviewed by Oprah Winfrey in 2021. (Chris Jackson/Getty Images)
“As a reasonable listener would understand it, [the] Defendant merely expresses an opinion about her childhood and her relationship with her half-siblings. Thus, the Court finds that Defendant’s statement is not objectively verifiable or subject to empirical proof,” District Judge Charlene Edwards Honeywell wrote.
The U.K.’s Daily Mail recently reported that the Duke of Sussex had quietly extended an olive branch to the royals by offering to share his official schedule of engagements. According to the outlet, this is a bid to ease tensions between him and his father.

Recent reports suggested that Prince Harry quietly extended an olive branch to the royals by offering to share his official schedule of engagements. (Karwai Tang/WireImage/Getty Images)
Fox News Digital reached out to a spokesperson for the Duke and Duchess of Sussex for comment. The couple’s office declined to comment when reached by People magazine.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP

Prince Harry told the BBC in May that he’s ready to reconcile with the royal family. (Max Mumby/Indigo/Getty Images)
But the chances of Meghan reconciling with her own family seem dim.
The mother of two has repeatedly accused Samantha and their father, former Hollywood lighting director Thomas Markle, of selling stories to the British tabloids. The Duke and Duchess cited the unbearable intrusions of the U.K. press and a lack of support from their palace as their reasons for their exit.

The Duke and Duchess of Sussex stepped back as senior royals in 2020 and moved to California. (Chris Jackson – Pool/Getty Images)
“I said, ‘I just need you to tell me and if you tell me the truth, we can help,’ and he wasn’t able to do that,” Meghan recalled to Winfrey, 71, about confronting her father about speaking with paparazzi.

The Duke and Duchess of Sussex spoke about their struggles with royal life a year after they made their exit. (Harpo Productions/Joe Pugliese via Getty Images)
At the time of the televised interview, which was viewed by nearly 50 million people globally, Meghan was expecting her second child.
“And that, for me, has really resonated, especially now as a mother,” she said. “I look at Archie, I think about this child [on the way], and I genuinely can’t imagine doing anything to intentionally cause pain to my child. I can’t imagine it. So, it’s hard for me to reconcile that.”
Fox News Digital’s Lauryn Overhultz contributed to this report.

